There are several top-tier relational database management system (RDBMS) platforms to choose from, but can they assist users in the set up and management of their databases?
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS), a product by Amazon Web Services (AWS), is a database-as-a-service (DBaaS) solution that maintains and optimizes an RDBMS.
RDS became one of the first DBaaS products widely available in 2009, and it remains one of the strongest options due to its security, integrations with Amazon’s other database tools, and customization capabilities.
See below to learn more about Amazon RDS.
A Closer Look at Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
- Database-as-a-service (DBaaS) software
- Amazon RDS features
- Amazon RDS integrations
- Benefits of Amazon RDS
- Amazon RDS use cases
- User reviews of Amazon RDS
- Amazon RDS pricing
- Amazon RDS competitors
Database-as-a-service (DBaaS) software
DBaaS software acts as the manager of an RDBMS, automating and handling database operations like setup, updates, and scaling through universal DBaaS abstractions that work with all of the supported databases.
When using a DBaaS, database administrators (DBA) don’t necessarily need to know all of the particulars of a database, such as programming language, location, and cluster sizes, to perform an instance, or action, in the database.
AWS explains that RDS is also designed to take care of some of the routine tasks usually handled by a DBA, like hardware provisioning, patching, and backups, so they can focus on higher-level database needs and optimizations.
See more: What is a Database Management System?
Amazon RDS features
Although RDS extends several features that help customers optimize databases, their most highly touted features show up at the implementation phase.
These top implementation features consist of Amazon RDS Management Console, AWS RDS Command-Line Interface, and simple API calls that make setup quick and easy. They also establish and outline settings and parameters for the preselected database. Even with limited knowledge about Amazon tools, RDS does most of the setup work before a user begins their launch.
Some other features of Amazon RDS include:
- Multiple read replicas
- Synchronous data replication
- Database snapshots
- SSD-backed storage options
- Automatic backups and host replacements
- Automatic software patching
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) access (encrypted IPsec VPN)
- Cloud implementation; or on-premises implementation through Amazon RDS on VMware
- Reserved instance and on-demand pricing
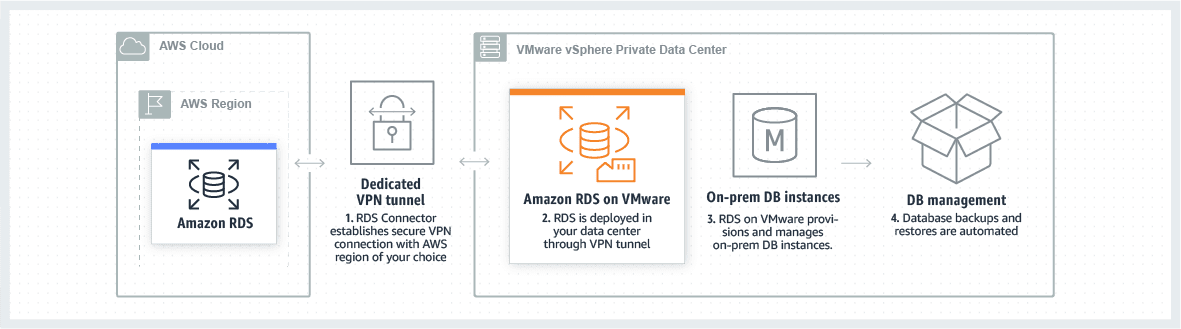
Amazon RDS integrations
As a database-as-a-service offering, Amazon RDS is specifically designed to integrate with several major RDBMS platforms.
Although some user reviews highlight a need for RDS to integrate with some lesser-known RDBMS platforms, RDS provides strong connections with and setup instructions for the following systems:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle Database
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Maria DB
- Amazon Aurora
More on Microsoft SQL Server: MS SQL Server Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) Review
More on Oracle Database: Oracle Relational Database Management System Review
Benefits of Amazon RDS
RDS offers many benefits to organizations that require some assistance in database setup, migration, monitoring, and security.
These are some of the top benefits RDS users are reporting:
- Launch savings: RDS reduces the time and complexity of launching an RDBMS
- Retained data: Strong disaster recovery features, such as snapshot restore and protecting data during migrations, upgrades, and other overhauls (expected and unexpected) in the system
- Data security: Frequent patching and security audits optimize overall RDBMS security
- Safeguarded access: Through the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and other security features like MFA, users can limit and manage who on the network can access databases
- Control service costs: Users only pay for the RDS features that they use, and depending on the number of instances that they require, they may be able to get away with free services for up to a year
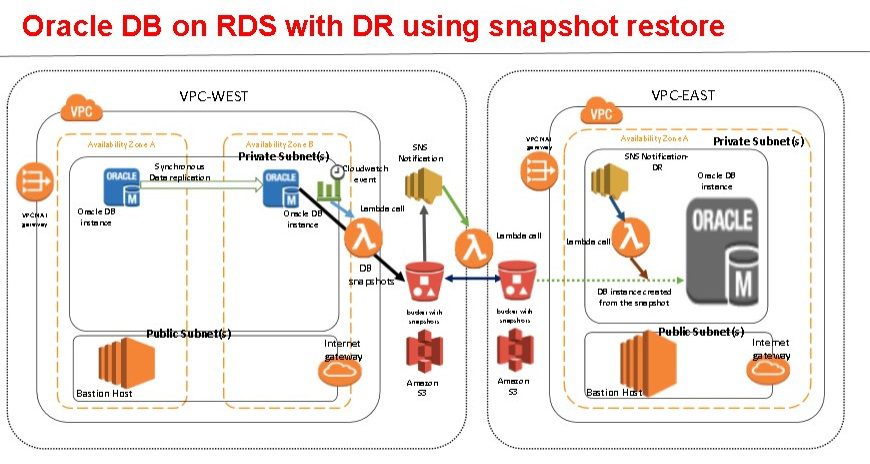
Amazon RDS use cases
Companies of all sizes and backgrounds rely on Amazon RDS to help them manage their databases, specifically in areas like secure data replication, cloud management, automated maintenance, and database optimization.
See what a few users have to say about their experience with RDS:
“Our appeals processing system, VACOLS, includes 20 million records stored in an Oracle 11g database. The system is more than 20 years old and is in the process of being modernized. During this time, we need to ensure that the data is securely replicated into the cloud for safekeeping. We’re using AWS DMS to replicate the database into an RDS Oracle database in AWS GovCloud, in a Multi-AZ deployment. This setup ensures that VACOLS data is preserved, secured, and highly available in the cloud, which is a serious win for VA and for our Veterans, who rely on us for the safeguarding of their information.” -Site reliability engineer, federal government, user review at AWS
“We’re a presentation software provider, and building a scalable database and storage system is not one of our competencies…With AWS, we don’t have to do any maintenance, and our databases automatically scale to fit our needs.” -Senior tools engineer, software industry, user review at AWS
“Using Amazon RDS for MySQL, we no longer need to spend time and money tuning IOPS to get strong database performance. By being in the cloud, we don’t need to worry about hardware acquisition costs. Ultimately, we have reduced our costs by 25%.” -Director of application development and cloud operations, software industry, user review at AWS
User reviews of Amazon RDS
Here are some of the top pros and cons users are highlighting about RDS:
| Review Site | Overall Score | Highlighted Pros | Highlighted Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| G2 | 4.6 out of 5 | Simple to provision/de-provision, scale up/down, resize, monitor, and automate Strong query and documentation features | Lack of log and debugging options Difficult setup and management of AWS console for beginners |
| Capterra | 4.8 out of 5 | Easy to manage alongside other AWS tools Stable and reliable in scalability and disaster recovery | Difficulty with replicating databases High learning curve for new users, especially on the dashboard |
| TrustRadius | 8.9 out of 10 | Little to no maintenance required by your team Several major database platforms to choose from | No root access to server Difficulty with accessing and searching logs |
| IT Central Station | 3.8 out of 5 | High availability for disaster recovery and management Administrative tasks are handled by the system instead of busy administrators | RDS should support additional databases Technical support usually requires an additional subscription |
In terms of weaknesses, some users express concerns about RDS features, both from beginner and expert perspectives.
Some beginners feel that features like the dashboard and query searching are too challenging without existing AWS knowledge or access to a database expert. Database experts, on the other hand, recognize there are limits to coding and customization to make the software more accessible, but some of them are frustrated by their limited access, particularly to logs.
Amazon RDS pricing
When a customer gets past the free trial period or moves into a paid package, they can select from several customizable pricing packages.
RDS does not require minimum purchases, and the customer only pays for the features they need. The pro: the customer isn’t overpaying for tools they don’t need or don’t know how to use. The hidden con: with so many features to choose from that adjust cost, the customer needs to know what they want and their budget so they don’t overbuy.
These are a few RDS package components that can change the total price:
On-demand vs. reserved instances
- On-demand instances: This is an option for companies running fewer instances or that don’t want a long-term commitment. The customer pays based on compute capacity by the hour their instance runs.
- Reserved instances: Companies can reserve a database instance for up to three-year terms, which gives them a significant discount but a stronger commitment to the software.
Database storage options
- General purpose (SSD) storage
- Provisioned IOPS (SSD) storage
- Magnetic storage
- Backup storage (by region)
Data transfer
- Internet to RDS
- RDS to internet
- RDS to other cloud apps
- RDS to other global locations
Companies can easily be overwhelmed when determining the price point of their exact RDS needs.
Potential users can try out this AWS pricing calculator to refine and check the product’s pricing.
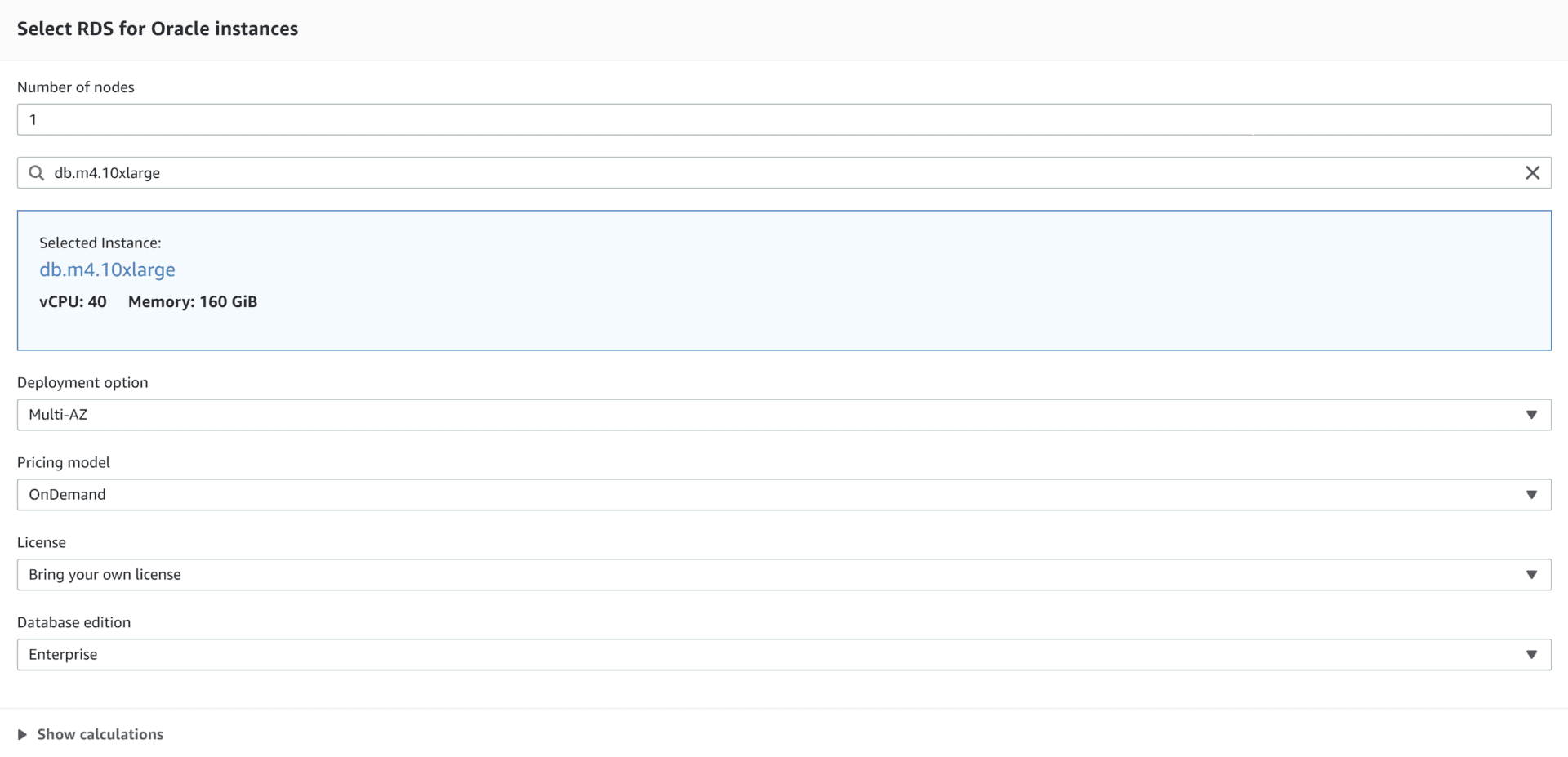
Amazon RDS competitors
RDS is one of the leading players in the quickly growing database-as-a-service market, which reached about $12 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15.7%.
At that rate, the market will more than double in the next few years and reach $24.8 billion by 2025, according to Markets and Markets Research.
These are some of the product’s top competitors in the DBaaS market:
- Oracle Database
- IBM Db2
- MongoDB Atlas
- SAP HANA
- Azure SQL Database
See more: Best Database Management Software 2020


