Vulnerability scanning is software that finds cybersecurity vulnerabilities in a company’s infrastructure, network, and software. Vulnerability scanning can also detect and patch these vulnerabilities, so cybercriminals cannot access a company’s network.
For this reason, vulnerability scans should be done daily. When conducting a scan, first choose the right software and then follow a defined set of policies and procedures to plug any threats.
See below to learn all about what vulnerability scanning is in the market:
Vulnerability Scanning Table Of Contents
- How Do Vulnerability Scanners Work?
- Why Perform Vulnerability Scans?
- What Are Vulnerability Scanning Best Practices?
- Should You Do Vulnerability Scanning Regularly?
- Vulnerability Scanning Software
- How to Conduct a Vulnerability Scan
How Do Vulnerability Scanners Work?
A vulnerability scanner is a vulnerability or risk testing tool that monitors for problems or coding flaws that seem to be cybersecurity problems.
If a vulnerability scanner tends to find more problems in one area, it will heavily focus on future and past vulnerabilities in the area. A user can choose which areas are most important to the company.
This can be done by using risk classification based on the data a company is protecting. This includes customer data as well. A company can set up their own policy as well adding rules, who can access the network for vulnerability scans.
Soon after, a company decides what kind of scan works best for them. Factors such as company size, budget, and scalability of the scan is vital to choose the proper scan for best protection.
Once the scan has been performed, a company will receive a report to see what exactly needs to be fixed and how to fix the problems. Using a vulnerability scan has many benefits and is a helpful step for cybersecurity in a company.
Why Perform Vulnerability Scans
Implementing vulnerability scanning as part of a cybersecurity strategy can save a company time, money, and crucial data.
“Vulnerability scanning is critical for a number of reasons,” said Russell Miller, CTO of Secure Access, OPSWAT, a cybersecurity company focused on critical infrastructure.
“Scanning for vulnerabilities and ensuring they are promptly remediated reduces the organization’s overall risk exposure to attacks, by exposing weaknesses in an organization’s endpoints or workloads.”
What Are Vulnerability Scanning Best Practices?
The recommendations from experts are extensive, but here are some examples of the best practices for companies interested in vulnerability scanning:
- Label company data and assets for scans: A business can identify the most vital data they want to protect through scanning.
- Conduct daily vulnerability scans: Experts recommend conducting vulnerability scanning every day, but companies can run their scans at different intervals, based on their configurations.
- Scanning everything necessary for the company: While a company can pick their priority data for scanning, experts recommend scanning all across software, hardware, cloud, and network systems to ensure their information is secure from any vulnerabilities.
- Use external tools to decrease vulnerabilities: Vulnerability scanning is a large part of a company’s security, but experts recommend also pairing it with other tools for better and broader protection.
See more: Simple Guide to Vulnerability Scanning Best Practices
Should You Do Vulnerability Scanning Regularly?
Experts recommend scanning for vulnerability every day or at least once a week. The more a network is tested, the more vulnerabilities can be detected before a cyberattack.
Joel Burleson-Davis, CTO at SecureLink, said companies should “scan everything, always.”
“We need to embrace continuous scanning or at least scanning with a periodicity that means there will be a short feedback loop from incident, to finding, to response,” Burleson-Davis said.
Vulnerability Scanning Software
Many technology companies have created their types of vulnerability scanning. These are some of the top vulnerability scanning software in the market:
- Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management
- Out of the following options Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management is considered the best overall vulnerability scanning tool, and it has a focus on medium to large businesses.
- SolarWinds Network Vulnerability Detection
- SolarWinds Network Vulnerability Detection is seen as the best option for backups of a company’s system, and works for every size of business from small to large businesses.
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is considered the best option for configuration audits for medium to large businesses.
- Rapid7 Nexpose
- Rapid7 Nexpose is considered the best vulnerability scanning tool, due to its consideration of customer’s company involvement. Rapid7 Nexpose can work for small, medium, and large businesses.
- IBM X-Force Red Vulnerability Management Services
- IBM X-Force Red Vulnerability Management Services is considered to be the best tool for hacker expertise. Along with the vulnerability scan, it will use a tool similar to penetration testing. They are used for small to large businesses.
- AWS Amazon Inspector
- Amazon Inspector is known for being the tool for the best discovery and routing the vulnerabilities. It is best for small to large organizations.
- Digital Defense Frontline VM
- Digital Defense Frontline VM is labeled as being the best for easy to use for companies new to vulnerability scanning. It is best for small, medium, and large businesses.
- Beyond Security beSECURE
- Beyond Security beSECURE is listed as the best vulnerability tool for three reporting levels. The product is best for small and medium companies.
- Tripwire IP360
- Tripwire IP360 is a vulnerability tool that offers both agentless and agent-based scanning. They work best for medium and large businesses.
- Acunetix by Invicti
- Acunetix by Invicti is a vulnerability scanning tool that is best for its automation processes. The tool is best suited for small, medium, and large companies.
See more: Best Vulnerability Scanning Tools
How To Conduct A Vulnerability Scan
1. Conduct And Analyze Risk Classification
When a company looks into vulnerability scans, it is vital to determine what part of the infrastructure needs to be scanned, starting with the riskiest assets. One way to determine risk classification is using low, medium, and high sensitivity. They are defined as:
- Low sensitivity: Data and assets that are accessible to the public, such as a company’s website, job listings, and product announcements.
- Medium sensitivity: Data and access that are meant to be internal, but if it is accessed by the public, it will not be catastrophic. Some examples are business plans, emails, and signed contracts.
- High sensitivity: Data and assets must be protected, if accessed by the public, it can be catastrophic for a business. Examples are customer information, financial records, and internal operation documents.
Once this information has been labeled, it is important to map out the areas of the network they are in, and how they can be accessed by IT teams.
2. Set Up Vulnerability Scanning Policies And Procedures
A vulnerability scanning policy is a document that outlines the processes and procedures followed when conducting a vulnerability scan. Common policies include establishing standards and implementing security controls. By creating an effective and easy-to-follow scanning policy, you’ll be able to achieve company communication benefits.
To keep networks and infrastructure secure, it is vital to set up policies and how the company plans to keep the information safe and protected from any cybersecurity threats.
To create a vulnerability scan policy:
- Make sure all employees are able to cooperate with the risk assessment. This includes educating employees, getting methods and ideas from employees, and confirming all employees are on board for their duties.
- All vulnerabilities must be identified and fixed to limit the risks. This will include detection of vulnerabilities from low, medium and high and patching these vulnerabilities for a clean slate.
- Complete an audit to:
- Ensure availability and safety of information and resources.
- Analyze possible security incidents and to help create a security policy.
- Monitor network and users to ensure safety of difficult areas.
- Be sure the vulnerabilities are addressed appropriately, if not, the infrastructure must complete an authenticated vulnerability assessment. It is helpful to know all strengths and weaknesses to ensure the system is fully addressed.
- Decide how often the system should be scanned. Companies usually decide between yearly, quarterly, and in some cases, monthly or daily. These options are available for ultimate detection during the scans.
- Map out what is sound and decide what systems should be scanned most often. As previously mentioned, this can be through ranking the vulnerabilities from low, medium, and high, or detecting specific areas that have the most common problems.
Once the policy is set up, employees and technology experts should be given the procedures that they should complete in the case of an attack. This can include patching, another scan, or even what they are responsible for.
3. Identify What Type(S) Of Vulnerability Scans A Company Wants To Use
There are several types of vulnerability scanning solutions available in the market:
| Types of Vulnerability Scanning |
Definition | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network vulnerability scanning | Find weaknesses on a network or infrastructure |
|
|
| Internal network vulnerability scan | Searches for vulnerabilities within a business network |
|
|
| Wireless vulnerability scanning | Finds vulnerable devices and passwords to identify problems with access points |
|
|
| External network vulnerability scan | Searches for vulnerabilities outside of a business network |
|
|
| Cloud vulnerability scanning | Tests for vulnerabilities within a cloud deployment |
|
|
| Database vulnerability scanning | Tests websites to identify weak points in a database |
|
|
Companies can pick which type is necessary for their business or use multiple types to get the best result.
4. Perform The Vulnerability Scan
Vulnerability scanners follow multiple steps in their execution process:
- Create security policies and controls and track data and other protected assets
- Scan systems for any vulnerabilities and classify their importance
- Pre-test vulnerability patches and apply to risk
- Patching for vulnerabilities has these steps:
- Test the infrastructure for any patches
- Have a security professional analyze patch stability
- Monitor patch updates
- Lay out a configuration management plan
- Patch any critical vulnerabilities
- Patching for vulnerabilities has these steps:
- Scan again to confirm the risk has been solved
Through these steps, a company is trusting the vulnerability scanner to keep their information and assets safe, both in the present and future.
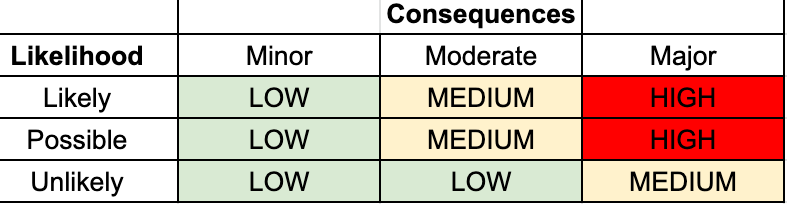
5. Interpret And Map Out The Vulnerability Scan Results
There are multiple ways to interpret vulnerability scan results, based on the software a company chooses to use. The most common steps to follow:
- Removing any duplicates and false positives
- Remediate any needed areas
- Prioritize unresolved vulnerability issues
As vulnerability scan software grows, the results may look similar to this:
Bottom Line
Vulnerability scanning is a tool that finds cybersecurity vulnerabilities in a company’s infrastructure, network, and software. There are multiple types of vulnerability scanners including wireless, cloud, and database vulnerability scanners.
Vulnerability scans are a necessary part of cybersecurity of a company’s network. When conducting a scan, a company must consider their network and the necessary vulnerabilities to fix.



